How to operate a drone effectively and safely is more than just understanding the controls; it’s about mastering a blend of technical skills, safety protocols, and legal awareness. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and navigation techniques to capturing stunning aerial footage and adhering to responsible flying practices. We’ll cover everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly and confidently.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive guide provides a structured approach to learning. We will explore various aspects, including flight planning, camera settings for optimal image quality, troubleshooting common issues, and navigating the legal and ethical considerations surrounding drone usage. By the end, you’ll have a solid foundation for operating a drone safely and effectively.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, and potential harm to people or property. This section details the essential steps and safety regulations to ensure a safe flight.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, a comprehensive inspection is vital. This involves checking the drone’s battery level, ensuring propellers are securely attached and undamaged, and verifying a strong GPS signal. Inspecting the drone’s body for any damage or loose parts is also essential.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to local laws and regulations regarding drone operation is paramount. This includes understanding airspace restrictions, maintaining a safe distance from people and property, and being aware of any no-fly zones. Responsible drone operation also means being mindful of privacy concerns and avoiding intrusive flights.
Pre-Flight Checklist Summary
| Checklist Item | Importance | Consequences of Neglect | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level Check | Ensures sufficient power for the flight. | Unexpected power loss, mid-flight crash. | Always use fully charged batteries and carry spares. |
| Propeller Inspection | Identifies damage that could lead to instability or failure. | Loss of control, crash. | Visually inspect propellers for cracks, chips, or damage before each flight. |
| GPS Signal Acquisition | Provides accurate positioning and stability. | Inaccurate flight, drift, loss of control. | Ensure a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS reception. |
| Visual Inspection of Drone | Detects any physical damage or loose parts. | Malfunction, crash. | Carefully examine the drone for any visible damage or loose components. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is essential for safe and effective operation. This section covers basic controls, various flight modes, and a step-by-step guide for beginners.
Drone Controls and Their Functions
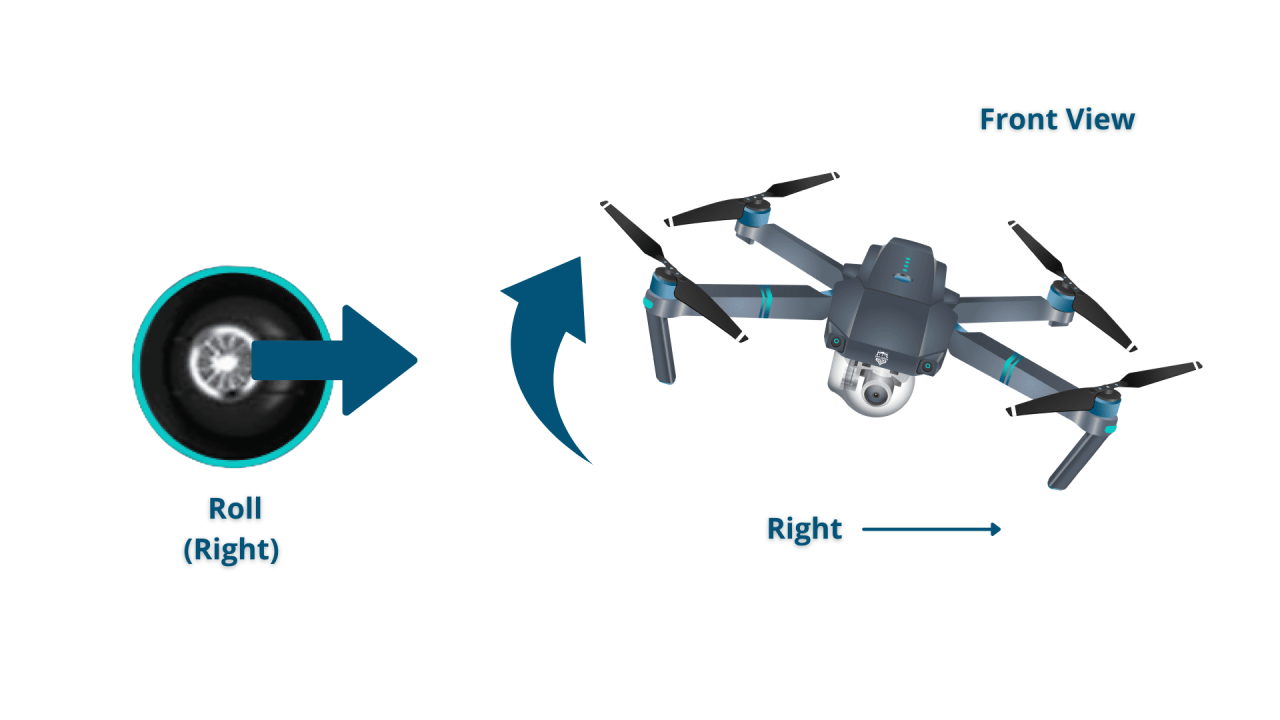
Most drones utilize two control sticks: one for controlling altitude and direction, the other for yaw (rotation) and movement. Buttons typically control features like camera functions, return-to-home, and flight mode selection. Understanding the function of each stick and button is crucial for mastering drone control.
Flight Modes and Maneuverability
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, providing a more stable and forgiving flight experience. Sport mode typically unlocks higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots. Understanding the differences between these modes is important for adapting to different flight situations.
Comparison of Control Schemes
While the basic principles of drone control are similar across models, specific control schemes and button layouts can vary. For instance, a DJI Mavic might have a dedicated button for camera control, while a Parrot Anafi might integrate these functions into the control sticks. Understanding these differences is crucial when transitioning between different drone models.
Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Ensure a strong GPS signal.
- Practice hovering by carefully adjusting the throttle stick.
- Practice moving the drone slowly in each direction (forward, backward, left, right).
- Gradually increase speed and complexity as your confidence grows.
Navigation and Flight Planning
Effective navigation and flight planning are essential for safe and efficient drone operations. This section details the use of GPS and other navigation systems, techniques for planning flight paths, and strategies for mitigating navigational challenges.
GPS and Navigation Systems

Most modern drones rely heavily on GPS for positioning and navigation. This allows for features like return-to-home and automated flight modes. However, GPS signals can be affected by factors like weather and interference, highlighting the importance of understanding potential limitations.
Flight Path Planning
Planning a flight path involves considering obstacles, airspace restrictions, and the drone’s battery life. This can be done manually or with the help of flight planning software. Safe flight path planning minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures efficient use of flight time.
Flight Planning Software and Apps, How to operate a drone
Several software applications and mobile apps assist in flight planning. These tools allow for visualizing the flight area, setting waypoints, and simulating the flight path before actual takeoff. Examples include Litchi, DroneDeploy, and DJI Fly. These applications often include features for mapping, obstacle avoidance, and airspace awareness.
Navigational Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
- Wind: Strong winds can affect drone stability and control. Mitigation involves choosing calm days for flights and adjusting flight parameters accordingly.
- GPS Interference: Obstructions or electronic interference can disrupt GPS signals. Mitigation includes flying in open areas with clear sky visibility.
- Battery Life: Always plan for sufficient battery life and include a buffer for unexpected events. Carrying extra batteries is crucial.
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section covers adjusting camera settings, choosing appropriate camera angles, and stabilizing footage.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Understanding aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for achieving optimal image quality. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO controls image sensitivity to light. Mastering these settings allows for capturing sharp, well-exposed images in various lighting conditions.
Camera Angles and Shots
Different camera angles and shots are suitable for various scenarios. High-angle shots provide a wide overview, while low-angle shots emphasize perspective and detail. Choosing the right angle and shot composition is key to creating visually appealing aerial media.
Stabilizing Footage and Minimizing Camera Shake
Drone cameras often incorporate image stabilization technologies to minimize camera shake. However, additional measures such as flying smoothly and using appropriate flight modes can further enhance stability. Post-processing techniques can also help stabilize footage.
Composing Visually Appealing Aerial Shots
- Use the rule of thirds for balanced composition.
- Utilize leading lines to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Incorporate interesting foreground elements to add depth.
- Choose appropriate lighting conditions for optimal image quality.
- Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for prolonging the lifespan of your drone. This section covers routine maintenance tasks, common malfunctions, and troubleshooting steps.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regular cleaning, proper battery care (avoiding extreme temperatures and overcharging), and careful storage are crucial for maintaining drone performance and longevity. Inspecting propellers, motors, and the drone’s body for damage after each flight is also recommended.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial for safe and effective operation; a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from takeoff and landing to advanced maneuvers. Ultimately, proficiency in operating a drone comes with practice and a solid understanding of the relevant regulations.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common issues include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor problems, and camera malfunctions. Understanding the possible causes of these issues is essential for effective troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Steps for Typical Issues
Troubleshooting involves systematically investigating the problem, checking connections, and trying different solutions. For instance, a low battery might require charging, while a GPS signal loss could indicate interference or a faulty GPS module. Understanding the troubleshooting steps for common issues is vital for quick resolution.
Common Drone Problems, Causes, Troubleshooting, and Prevention
| Problem | Likely Cause | Troubleshooting Steps | Preventative Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, high power consumption. | Charge the battery, check power settings. | Use fully charged batteries, fly in optimal conditions. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, interference, faulty GPS module. | Move to an open area, check GPS module. | Fly in open areas with clear sky visibility. |
| Motor Problems | Motor damage, loose connections. | Inspect motors, check connections. | Avoid crashes and rough landings. |
| Camera Malfunction | Loose connections, software glitches. | Check connections, restart drone. | Handle the drone carefully. |
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to legal and ethical guidelines. This section covers relevant laws, ethical implications, and best practices for responsible drone use.
Laws and Regulations Governing Drone Operation
Drone laws and regulations vary by location. These regulations often cover airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations. Understanding these rules is crucial for legal compliance.
Ethical Implications of Drone Use
Ethical considerations include respecting privacy, avoiding intrusive flights, and being mindful of potential impacts on the environment. Responsible drone operators prioritize safety and minimize any potential negative consequences.
Permits and Licenses for Commercial Drone Operation
Commercial drone operations often require specific permits and licenses. These requirements ensure that commercial drone pilots meet certain standards of competency and safety. Obtaining the necessary permits is essential for legal commercial drone use.
Best Practices for Ethical and Legal Compliance
- Register your drone with the relevant authorities.
- Obtain necessary permits for commercial operations.
- Always respect privacy and avoid intrusive flights.
- Adhere to all local laws and regulations.
- Fly responsibly and safely.
Advanced Drone Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
This section explores advanced drone maneuvers, features, and applications.
Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers such as flips, rolls, and precision hovering require significant skill and practice. These maneuvers are typically performed in open areas with ample space and under controlled conditions. Mastering these techniques expands the capabilities of the drone for creative filming or specific tasks.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful planning and practice, and a good starting point is learning the basics by checking out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This resource will equip you with the knowledge to confidently and safely control your drone, ensuring a positive and productive flying experience.
Advanced Features

Advanced features like waypoint navigation allow for automated flight paths, while automated flight modes such as “follow me” or “orbit” offer convenient filming options. These features enhance the drone’s functionality and efficiency.
Applications of Drones
Drones have found widespread applications in various fields. Photography and videography are popular uses, but drones also play crucial roles in inspection, delivery, agriculture, and search and rescue operations. The versatility of drones continues to expand as technology advances.
Drone Software for Advanced Flight Planning and Data Analysis
Specialized software allows for advanced flight planning, data analysis, and integration with other systems. This software can process data collected during flights, enabling advanced applications such as 3D mapping, thermal imaging analysis, and precision agriculture.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical expertise with a strong sense of responsibility. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of safe and legal drone flight, from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques. Remember, consistent practice, adherence to regulations, and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Embrace the skies responsibly, and capture breathtaking aerial perspectives with confidence and skill.
Popular Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functionality.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and usage. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes of flight time per battery.
What happens if I lose the GPS signal during flight?
Most modern drones have a “return to home” (RTH) feature that will automatically bring the drone back to its starting point. However, always maintain visual contact with your drone.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and regulations.
